Approach from the Natural Sciences Perspective
In order to approach history and archaeology from a scientific aspect, the Centre for Hiraizumi Studies have been introduced analytical equipment and three-dimensional measuring instruments.
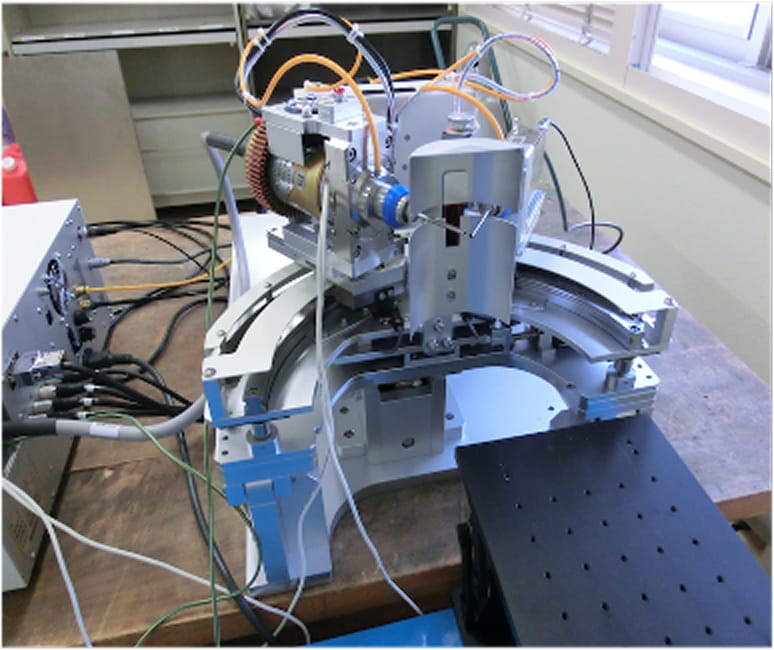
-
X-ray diffractometer
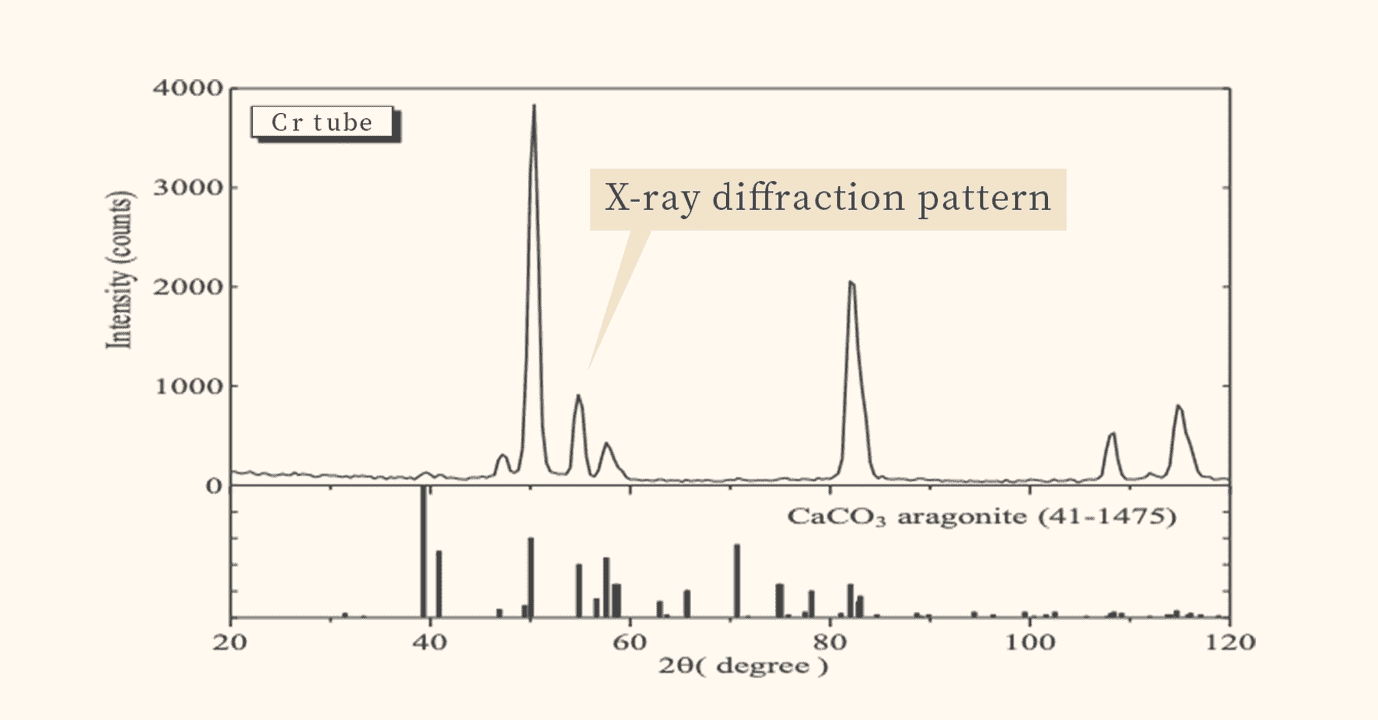
The X-ray diffraction pattern is used to find out what kind of material the object is made of.
-
What the analysis reveals
The analysis equipment provides information on the chemical structure and chemical species of artefacts and excavated objects. It enables non-destructive analysis while carrying out 'in situ analysis' without removing cultural or archaeological material from the site.
For example, it can distinguish between ferrous oxide (FeO) and ferric oxide (Fe2O3). -
Measuring method
X-ray diffractometers irradiate the analyzed sample with X-rays to obtain information on the crystals and minerals in the sample.
-
-
Portable combined X-ray diffractometer
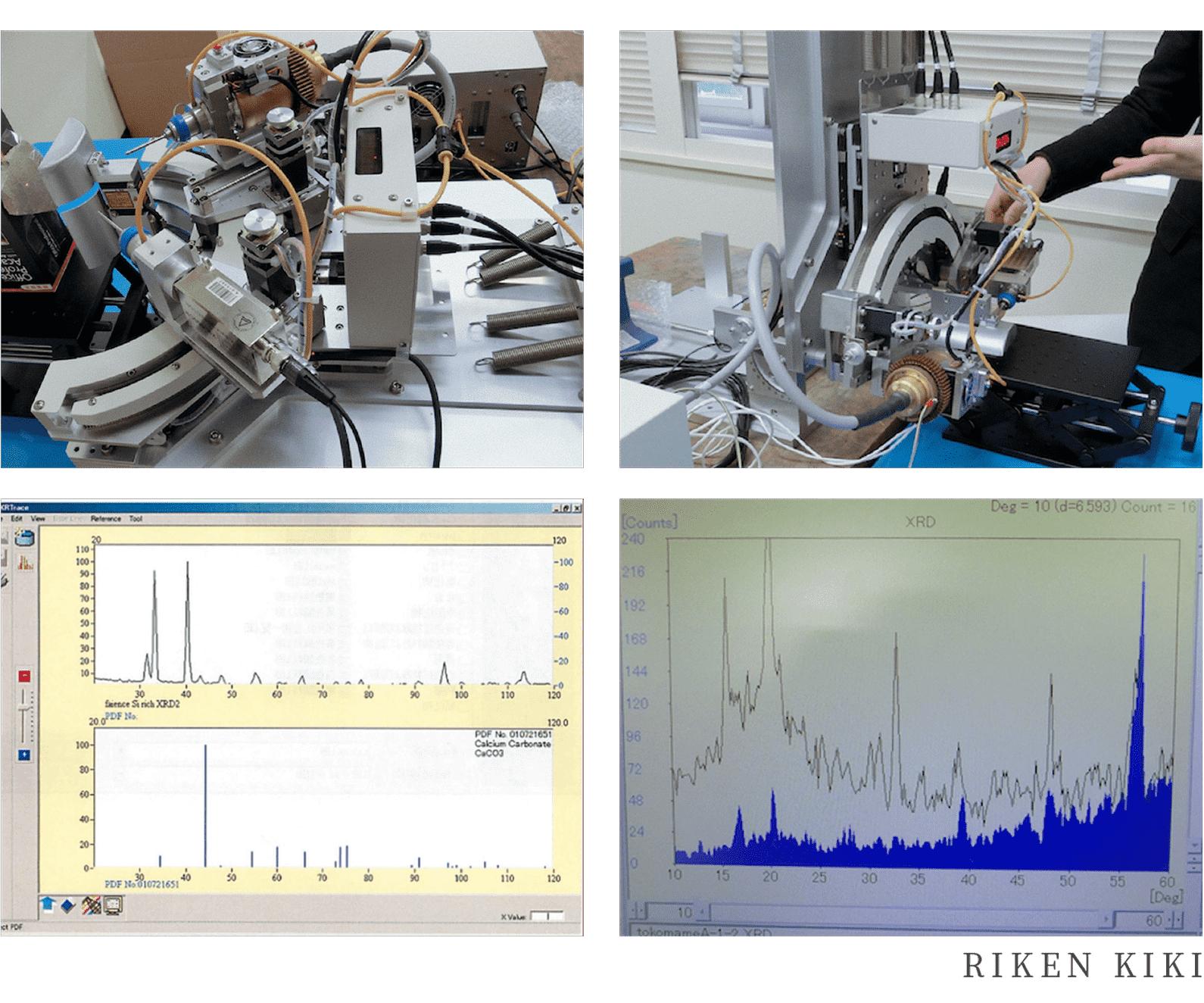
-
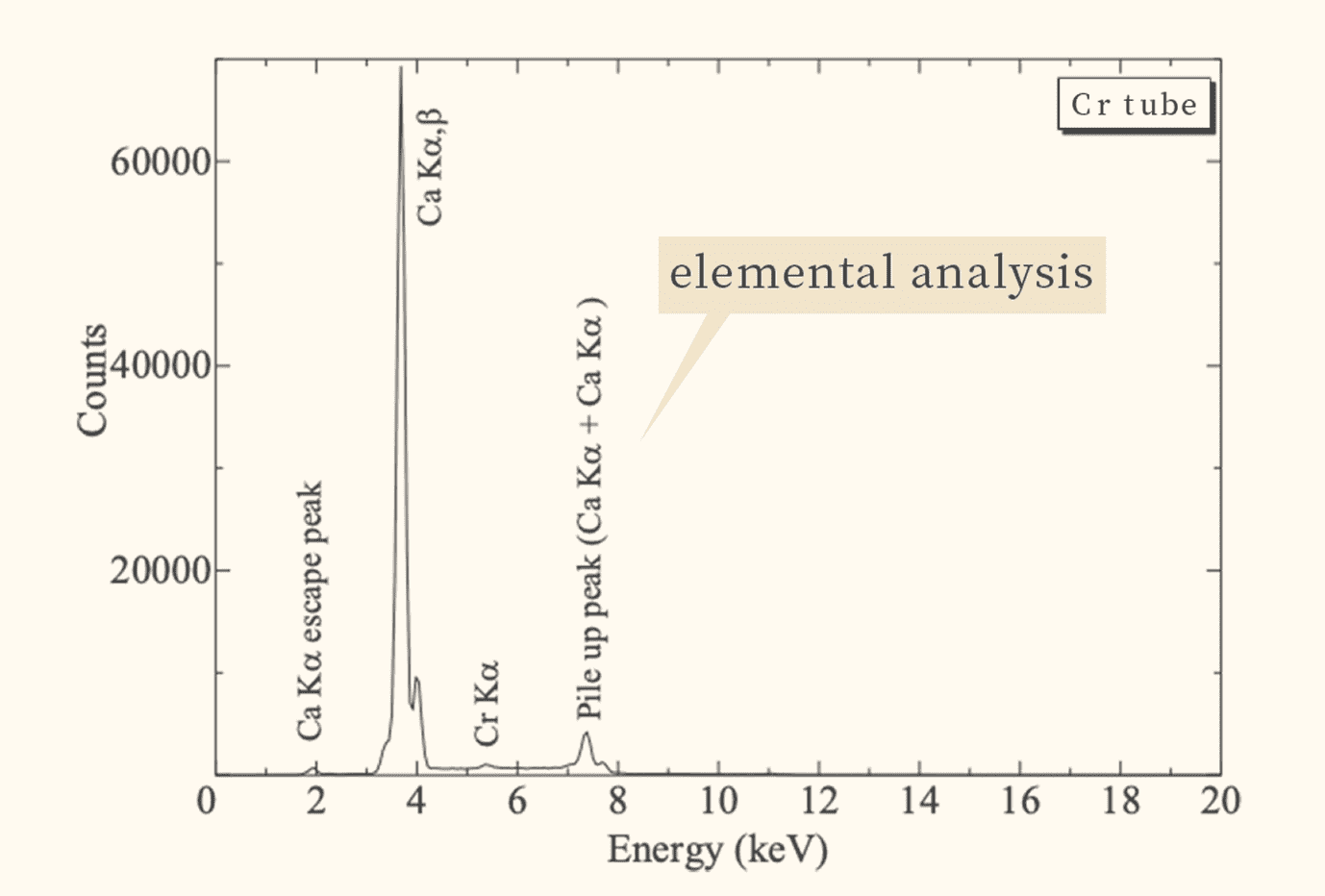
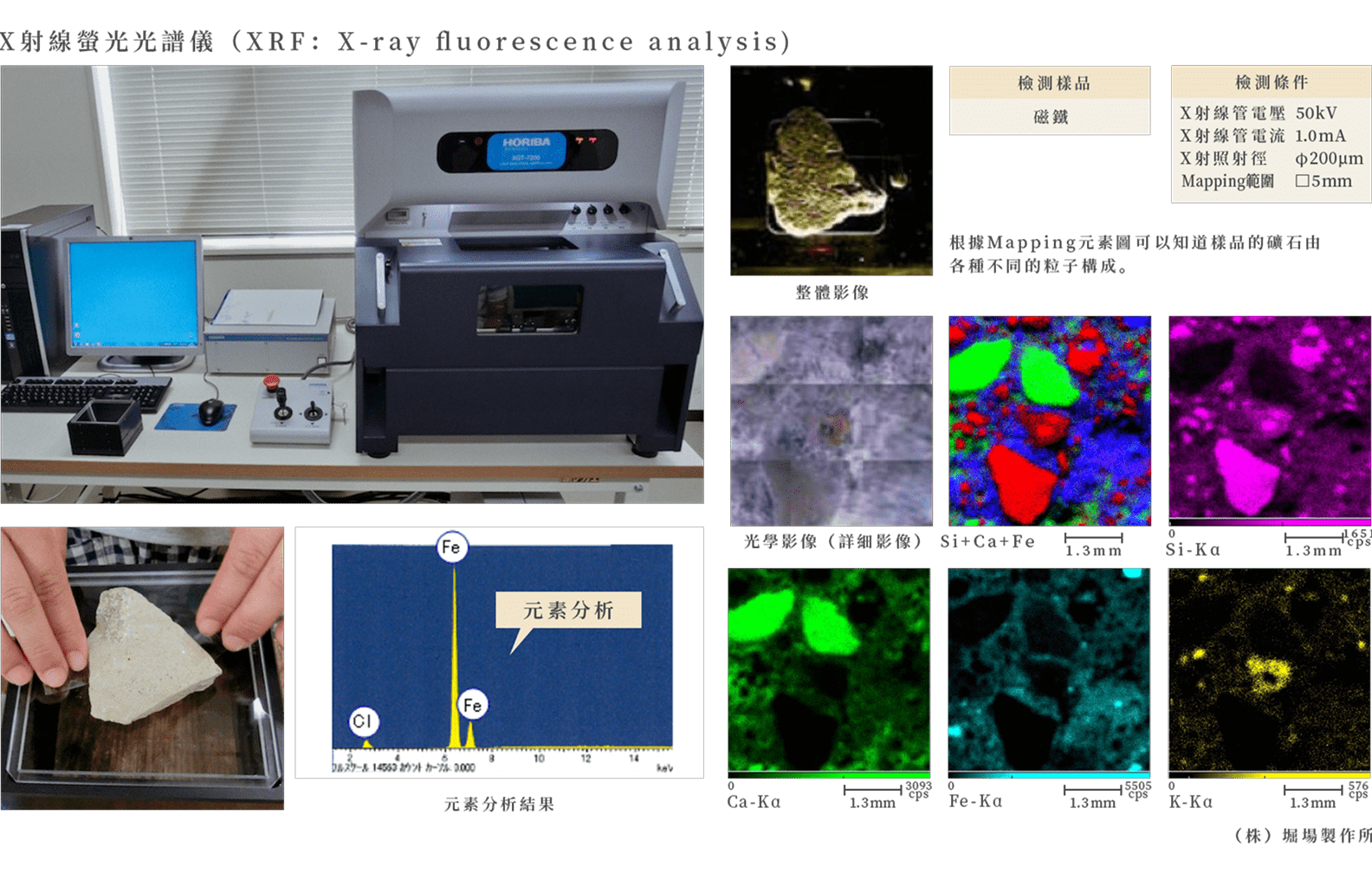
X-ray fluorescence analyzer
Elemental analysis to find the type and concentration of elements.
-
What the analysis reveals
This analysis equipment provides elemental information on the type and concentration of elements contained in artefacts and excavated objects.
In combination with an X-ray diffractometer, the identity of most materials can be determined. -
Measuring methods
X-ray fluorescence analyzers can perform qualitative and quantitative analysis on non-destructive samples by irradiating the analyzed sample with X-rays.
-
-
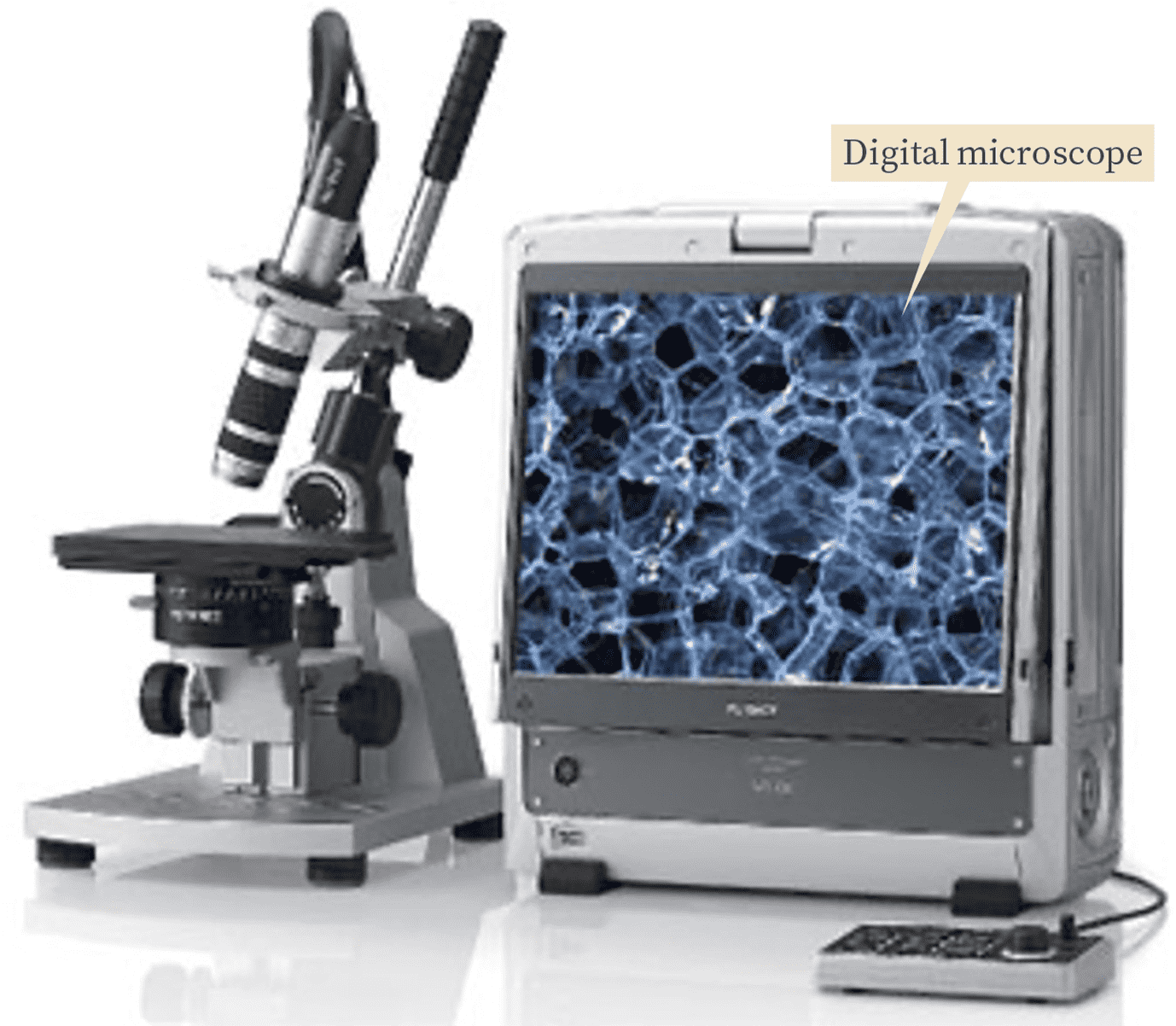
Digital microscope
Explore visually through magnification
-
What the analysis reveals
Visually magnify surfaces and minute objects of excavated objects to a size that is visible to the naked eye for microscopic observation.
-
Measuring method
Solid samples can be observed as they are.
-
-
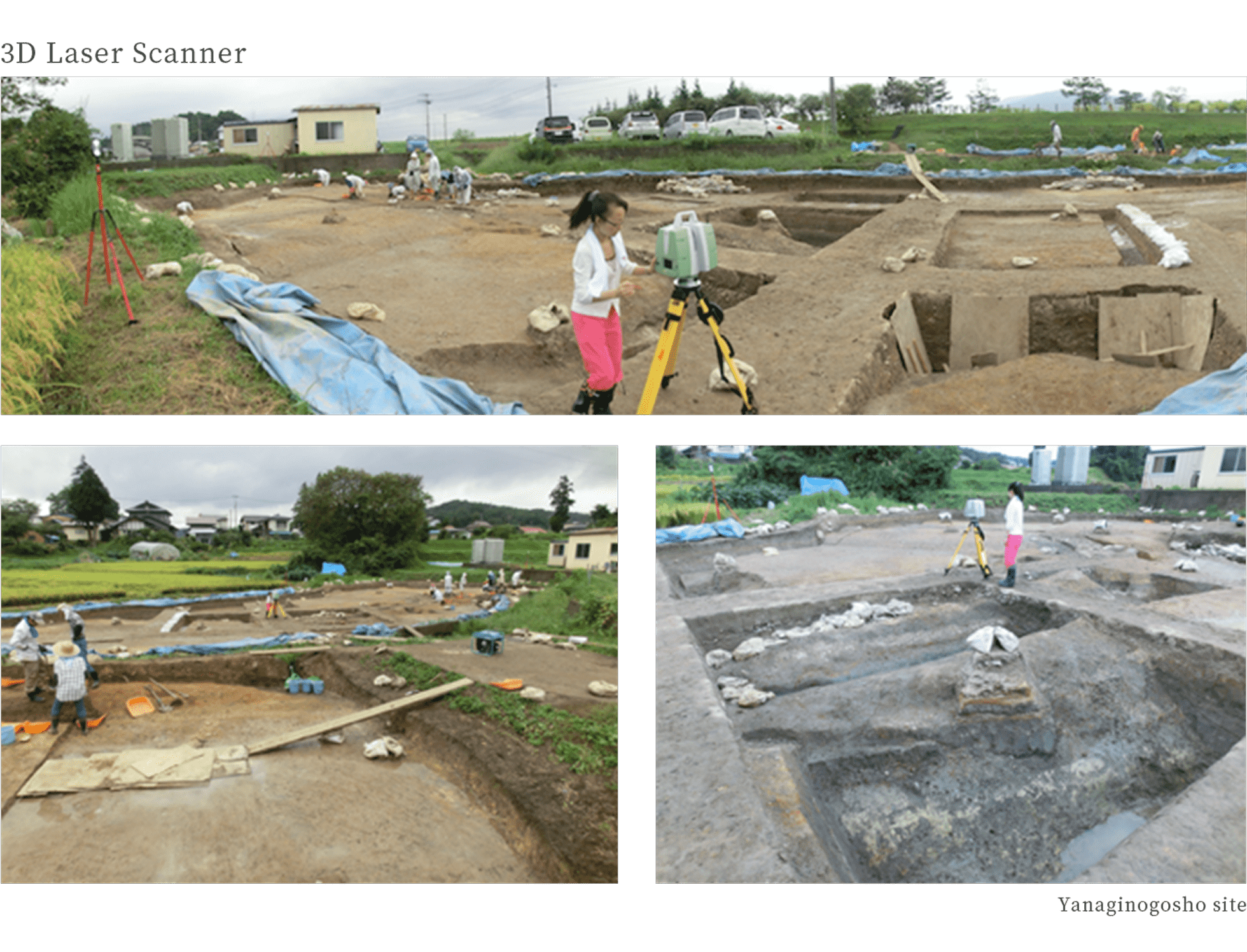
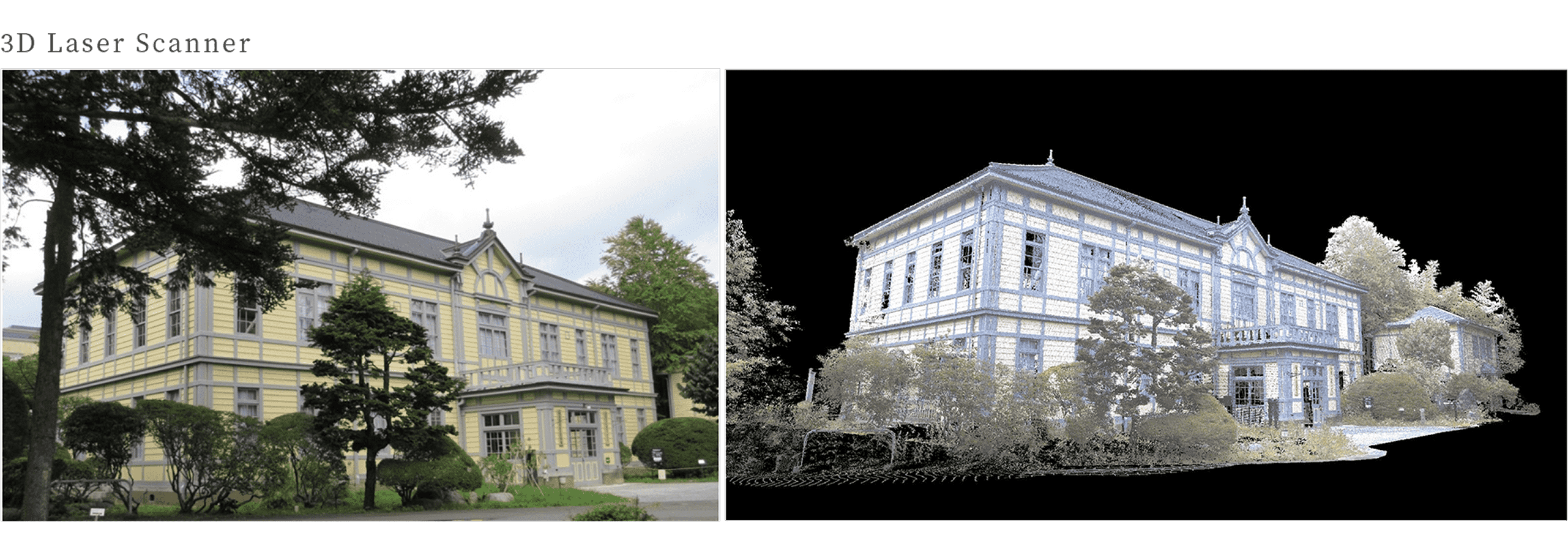
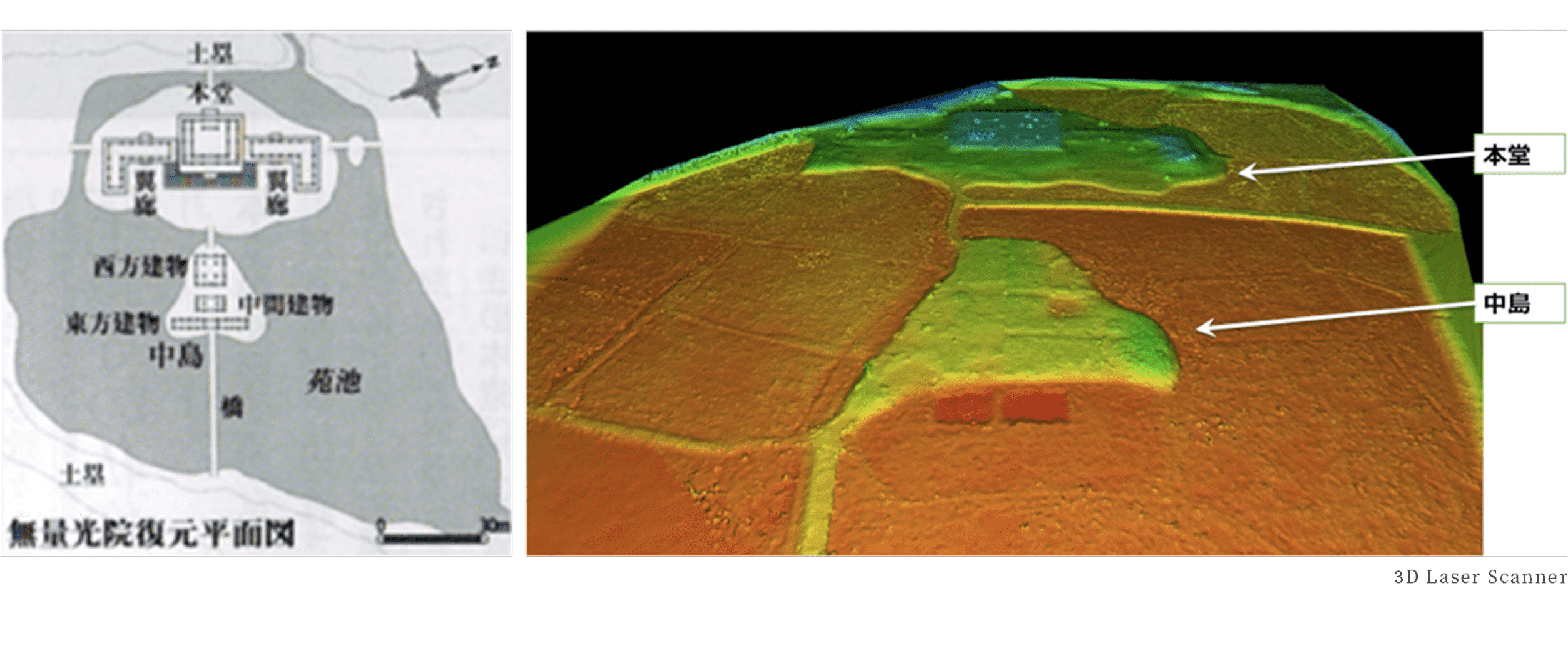
3D laser scanner
Digitalizing archaeological sites, remains and cultural properties at high speed and with high accuracy.
-
What you can do with measurement
By converting archaeological sites, remains, gardens and cultural properties into digital data, their shape and topography can be connected to the future.
In addition, as this data can be converted into three dimensions, it is possible to virtually reproduce the measured objects on a display. -
Measuring method
The 3D laser scanner emits a laser beam at the object to be measured, such as an archaeological site, and recognizes the distance and direction of the object from the bounced back signal.
The recognized data is recorded in the form of point-state co-ordinate values. As the entire object is measured from all angles, it is expressed in many coordinate values, so the data after measurement is called [point cloud data].



-
